Charging station types
The Type 2 charging station is the most common charging station for electric vehicles in public and private areas.
They are available in a wide variety of versions with permanently installed charging cables or with a connection socket.
The latter also enables vehicles with a Type 1 inlet on the vehicle to charge electricity.
Which charging capacities are realized depends on the connected load and the charging speed at which the vehicle to be charged can be charged.
The choice of charging cable often also determines the maximum charging capacity that can be used by the vehicle.
The following always applies: the weakest link in the chain of charging station, charging cable and vehicle decides how fast charging takes place.
Example:
An electric car charges at a charging station with 22 kW AC charging power.
The car can use the full 22 kW for charging.
However, a charging cable is used that only charges with max. 7.4 kW enables (e.g. charging cable: 32A 1-phase). The charge is then 7.4 kW.

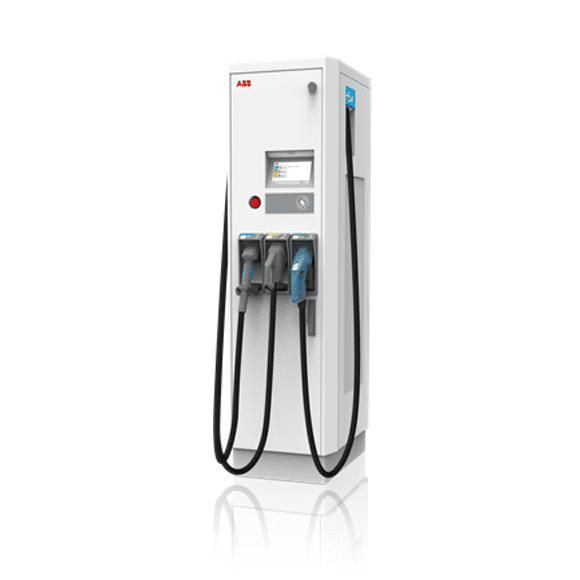
Multi-standard quick charging stations (dual or triple charger) are large charging stations that combine several charging standards and are designed to carry out quick charging with alternating current and / or direct current.
As a rule, these charging stations combine the CCS and CHAdeMO standard – i.e. they are pure direct current (DC) charging stations or they are also designed with the Type 2 (AC) standard (type 2 standard socket or fixed type 2 charging cable). Here mostly with charging capacities of up to 22 kW or 43 kW.
At these charging stations, charging is usually a matter of around 30-90 minutes (depending on the battery temperature and vehicle / battery size).
With the increasing availability of vehicles with a larger battery capacity (e.g. 64 kWh), these charging stations are becoming increasingly important when it comes to quickly charging the battery.
Various shopping centers or discounters usually provide charging stations of this type as a service for your customers during shopping, usually free of charge (e.g. Lidl Austria, ALDI Süd).

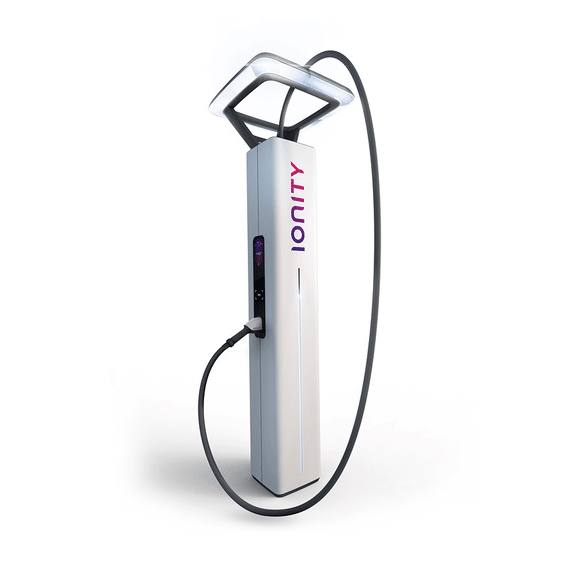
The high-power chargers (high-performance quick-charging stations) are generally charging stations that go beyond the previous general fast-charging power of 50 kW. Charging stations that offer charging capacities of 70 kW and more therefore fall into this area.
The Tesla Superchargers and those of the provider IONITY are particularly well known in Europe.
Depending on the variant, they offer charging capacities from 100 to 350 kW.
Due to the necessary specifications, for example. all IONITY HPC charging stations are exclusively equipped with Combo 2 (CCS) charging standard.
Suppliers such as Fastned also offer CHAdeMO with a charging power of 150 kW – not least because of the decreasing selection of vehicles with CHAdeMO charging standard (e.g. Nissan Leaf / eNV 200), these are becoming less and less important for Europe.
Since the introduction of the Model 3, the Tesla Superchargers have also increasingly relied on the Combo 2 (CCS) charging standard, but continue to allow charging only for their own vehicle fleet.
At these charging stations, charging is usually a matter of around 20-45 minutes (depending on the battery temperature and vehicle).
Especially for longer journeys / trips, these charging stations are specifically controlled to guarantee that you can continue driving as quickly as possible.
That is why most HPC charging stations are located along busy motorways, at rest stops or traffic hubs all over Europe.
The HPC charging stations are of particular importance with regard to the breakthrough of a mass distribution of e-mobility.

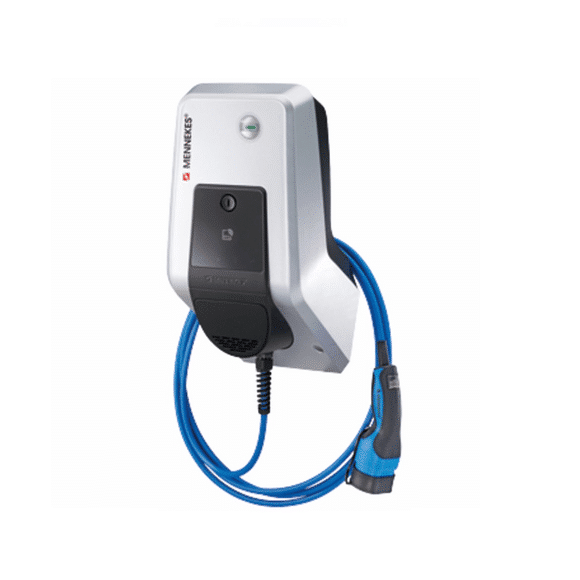
A wallbox is a charging station that is mounted or fixed on the (house) wall.
The term wall charging station is usually also used.
Wallboxes are usually charging stations with type 2 plugs or sockets, which generally provide up to 22 kW alternating current (AC) for charging electric vehicles.
They are usually found in the private sector or at hotels and shopping centers.
Charging stations at the latter locations are also known as destination charging.
The industry is working on the mass-marketable (affordable) implementation of DC wallboxes with charging capacities of around 20 kW.
Due to the increasing spread of e-mobility, the number of wall boxes in the area of shopping centers or company fleets continues to increase. It is likely that the establishment of charging infrastructure will also be anchored in law.
The establishment of (fast) charging infrastructure is already being financially supported in some countries.

Mobile charging stations are compact and portable charging stations in which the technology required for a charging station is housed in a small space.
Their main advantage is that they can be taken anywhere and that there are usually no larger installations at home.
This allows greater flexibility when loading while traveling or on the go.
The technical measures prescribed for personal protection, such as residual current circuit breakers (FI), temperature monitoring, adapter detection with automatic power reduction, etc. are already integrated ex works.
Additional adapters allow operation at weaker or non-local sockets (e.g. England).
The term ICCB, IC-CPD or mobile, intelligent charging cable is also used for some mobile charging stations.
In Austria, the purchase of mobile charging stations, such as wall boxes, is also financially supported by the federal government and, if applicable, the federal states as part of an e-vehicle promotion.
Well-known mobile charging stations are the NRGkick and the go-eCharger.

In the meantime, many modern electric vehicles are equipped with integrated navigation systems that use certain databases / charging station directories to include them in the navigation.
Often, however, the databases on the locations where charging stations can be found are outdated or inadequate.
Over the past few years, the EV community has therefore taken on the task of developing apps that can be used to find charging stations and navigate there, regardless of the vehicle.
Due to our expertise and our many years of professional and private experience, we can currently recommend two apps especially if you are looking for the right charging station for your e-vehicle.
NextPlug:
The NextPlug app is a free app for Android systems that accesses the GoingElectric database.
It is one of the most advanced charging station directories and offers a wide range of options for finding the right charging station for your own vehicle.
NextPlug is available for download from the Google Play Store: Next Plug downloaden
chargEV:
The chargEV app is a free app for iOS systems that also accesses the GoingElectric database.
By adapting to iOS, the app is very easy to use and also offers options for filtering certain charging station types (e.g. only quick charging stations, etc.).
It is available for download from the App Store: chargEV downloaden
In recent years, numerous mobility service providers, charging station operators (CPOs) and initiatives have been developed that offer charging electricity tariffs / contracts for charging – including charging cards and app support.
Cross-border roaming partnerships, similar to those used in mobile telephony, make it possible to charge a contract with other providers at certain charging rates.
It is therefore important to find out exactly from which providers you want to be a customer, which roaming partners support them and what the charging costs there.
The chargeprice (formerly plugchecker) page offers a good overview of the different providers and how much which charging station costs which provider.

 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Mennekes charging cable Type 2 | 32A | 22kW (3ph.) | 7,5m
Mennekes charging cable Type 2 | 32A | 22kW (3ph.) | 7,5m  Mennekes charging cable Type 2 | 32A | 22kW (3ph.) | 4m
Mennekes charging cable Type 2 | 32A | 22kW (3ph.) | 4m